【8.3】通过VCF文件制作定制化的参考基因组
最近做的项目要对reference genome基于突变进行一些modify,制作personalized genome或者说是psuedo-genome伪基因组。其实就是把某个测序样本call出来的SNP && indel替换掉参考基因组对应位置的碱基。
自己可以编写脚本修改,使用Perl中的substr来进行单个位点修改,把坐标按照从后往前的顺序,而不是从前到后。
其实有蛮多工具可以做这个的,在这里安利一下,大家可以使用体验一下。
一、GATK FastaAlternateReferenceMaker
GATK作为通用的变异检测的软件,其中有很多有用的工具,这里介绍一下FastaAlternateReferenceMaker: Create an alternative reference by combining a fasta with a vcf.
准备好检测的VCF文件,参考基因组FASTA文件,使用如下命令:
/gatk_software_path/gatk FastaAlternateReferenceMaker \
-R /ref_genome_path/reference-genome.fasta
-O /ref_genome_path/psuedo-genome.fa \
-L input.intervals \
-V /variant_path/input.vcf \
[--snp-mask mask.vcf]
这里的-L参数可以多单个基因或者基因组一段区域进行替换。
–snp-mask参数,当构建时psuedo-genome.fa时,该VCF文件中的SNP用作掩码(在序列中插入N)。
运行结束,个人的参考基因组就构建好了,一般制作psuedo-genome.fa就是为了消除变异带来的影响,部分其他参数可以到gatk官网查阅。另外FastaAlternateReferenceMaker使用简单的indel,当VCF文件包含复杂的位点时(complex substitutions),会忽略。 PS:
If there are multiple variants that start at a site, it chooses one of them randomly.
When there are overlapping indels (but with different start positions) only the first will be chosen.
我得案例:
gatk FastaAlternateReferenceMaker -R /opt/ref/ref.fasta -V ${output}/${ID}/${ID}.vcf -O ${output}/${ID}/${ID}.genome.fasta
二、perEditor
perEditor用于分析phased SNPs/indels,意味着VCF文件中的GT是0|1/1|1/1|2,而不是我们常见的0/1这种,明确知道变异是在母本还是父本染色体上,第一个是母本,第二个是父本,使用方式如下:
perEditor ref_genome.fa snps_indels.vcf allele indivicual personalized_genome.fa
perEditor chr1.fa variations.vcf mother 1 chr1_customized.fa
这里对参数进行一下解释:
- allele两个选项mother|father,代表等位基因来自于哪一个亲本;
- indivicual,整数,这个是因为有一些VCF文件中不止包含一个样本的突变信息,参数代表选择第几个样本的突变来进行创建personalized genome,1代表第一个样本;


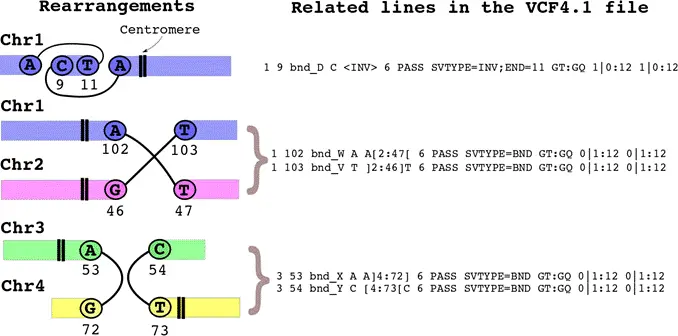
perEditor_ra,允许用户把染色体重排信息考虑到创建个性化参考基因组中,一样只服务于phased的数据,另外还需要把涉及染色体重排的染色体放在一个目录下:
$ ls chr*fa
chr1.fa chr2.fa chr3.fa chr4.fa
$ perEditor_ra rearrangements.vcf chr_length.bed centromeres.bed individual allele
$ perEditor_ra rearrangements_t.vcf chr_length_t.bed centromeres_t.bed 1 father
这里的individual和allele参数和perEditor是一样的含义; rearrangements_t.vcf,染色体重排注释结果,vcf format version 4.1; chr_length_t.bed,文件中包含基因组每一条染色体的长度,即核苷酸总数,格式如下:
chr1 200
chr2 104
chr3 154
chr4 102
centromeres_t.bed,文件中包含每条染色体的着丝粒位置的文件,着丝粒坐标用于确定新染色体的身份,当两条染色体由于重排而合并时,新染色体将按照着丝粒来源的名称来命名,继承两个着丝粒,其名称则包含两个亲本染色体的名称,文件格式如下:
chr1 50 60
chr2 15 20
chr3 20 30
chr4 80 90
bed文件和vcf文件位于同一个工作目录下,最终生成的新的染色体命名中添加了new:
$ ls *new*fa
chr1_new.fa chr2_new.fa chr3_new.fa chr4_new.fa
三、g2gtools
g2gtools通过将SNP和indels整合到参考基因组中来创建自定义基因组,提取感兴趣的区域(例如外显子或转录本),并在两个基因组之间转换文件(bam,gtf,bed)的坐标。 与其他liftover 工具不同,g2gtools不会丢弃掉落在indel区域上的alignments。 版本0.2可以创建个人二倍体基因组。 新版本仍然将个人基因组坐标上的二倍体比对转换回参考基因组,因此我们可以比较种群样本之间的比对。
安装
$ conda config --add channels r
$ conda config --add channels bioconda
$ conda create -n g2gtools python=2 jupyter ipykernel
$ source activate g2gtools
$ conda install -c kbchoi g2gtools
Usage
先激活virtual environment:
source activate g2gtools
创建自定义的基因组,需要下列信息:
${REF} reference genome in fasta format
${STRAIN} strain name (usually a column name in the vcf file)
${VCF_INDELS} vcf file for indels
${VCF_SNPS} vcf file for snps
${GTF} gene annotation file in gtf format
下面是操作流程:
# 创建映射两个基因组之间的碱基的chain文件
g2gtools vcf2chain -f ${REF} -i ${VCF_INDELS} -s ${STRAIN} -o ${STRAIN}/REF-to-${STRAIN}.chain
# 把snp添补到ref genome上
g2gtools patch -i ${REF} -s ${STRAIN} -v ${VCF_SNPS} -o ${STRAIN}/${STRAIN}.patched.fa
# 将indels整合到snp添补后的基因组中
$ g2gtools transform -i ${STRAIN}/${STRAIN}.patched.fa -c ${STRAIN}/REF-to-${STRAIN}.chain -o ${STRAIN}/${STRAIN}.fa
# 针对新的定制基因组创建定制基因注释
$ g2gtools convert -c ${STRAIN}/REF-to-${STRAIN}.chain -i ${GTF} -f gtf -o ${STRAIN}/${STRAIN}.gtf
$ g2gtools gtf2db -i ${STRAIN}/${STRAIN}.gtf -o ${STRAIN}/${STRAIN}.gtf.db
四、vcf2diploid
vcf2diploid通过将phased的变异整合到参考基因组中,从vcf文件创建二倍体基因组。
Installation
git clone https://github.com/abyzovlab/vcf2diploid.git
cd vcf2diploid
make
Running
java -Xmx10g -jar vcf2diploid.jar -id sample_id -chr file1.fa file2.fa ... [-vcf file1.vcf file2.vcf ...] > logfile.txt
OPTIONS:
id - (required) the ID of individual whose genome is being constructed (e.g., NA12878). The tool recognizes by this ID in the VCF file
chr - (required) FASTA file(s) of reference sequence(s)
vcf - (required) VCF4.0 file(s) containing variants from parents and the individual
Xmx - max memory allocation for JAVA. In this example, 10GB was allocated.
logfile.txt - stores the standard output produce from the run
五、bcftools consensus
Usage
About: Create consensus sequence by applying VCF variants to a reference fasta
file. By default, the program will apply all ALT variants. Using the
--sample (and, optionally, --haplotype) option will apply genotype
(or haplotype) calls from FORMAT/GT. The program ignores allelic depth
information, such as INFO/AD or FORMAT/AD.
Usage: bcftools consensus [OPTIONS] <file.vcf>
Options:
-c, --chain <file> write a chain file for liftover
-e, --exclude <expr> exclude sites for which the expression is true (see man page for details)
-f, --fasta-ref <file> reference sequence in fasta format
-H, --haplotype <which> choose which allele to use from the FORMAT/GT field, note
the codes are case-insensitive:
1: first allele from GT
2: second allele
R: REF allele in het genotypes
A: ALT allele
LR,LA: longer allele and REF/ALT if equal length
SR,SA: shorter allele and REF/ALT if equal length
-i, --include <expr> select sites for which the expression is true (see man page for details)
-I, --iupac-codes output variants in the form of IUPAC ambiguity codes
-m, --mask <file> replace regions with N
-o, --output <file> write output to a file [standard output]
-s, --sample <name> apply variants of the given sample
Examples:
# Get the consensus for one region. The fasta header lines are then expected
# in the form ">chr:from-to".
samtools faidx ref.fa 8:11870-11890 | bcftools consensus in.vcf.gz > out.fa
定制基因组
$ bcftools consensus <file.vcf> \
--fasta-ref <file> \
--iupac-codes \
--output <file> \
--sample <name>
# Apply variants present in sample "NA001", output IUPAC codes for hets
$ bcftools consensus -i -s NA001 -f in.fa in.vcf.gz > out.fa
# Create consensus for one region. The fasta header lines are then expected
# in the form ">chr:from-to".
$ samtools faidx ref.fa 8:11870-11890 | bcftools consensus in.vcf.gz -o out.fa
六、vcfutils.pl
samtools、bcftools和vcfutils.pl三个程序联合使用,从BAM文件开始操作,到获得新的参考基因组:
$ samtools mpileup -d8000 -q 20 -Q 10 -uf REFERENCE.fasta Your_File.bam | bcftools call -c | vcfutils.pl vcf2fq > OUTPUT.fastq
# d, --max-depth
# -q, -min-MQ Minimum mapping quality for an alignment to be used
# -Q, --min-BQ Minimum base quality for a base to be considered
$ sed -i -e '/^+/,/^\@/{/^+/!{/^\@/!d}}; /^+/ d; s/@/>/g' OUTPUT.fastq
References
参考资料
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/a3b0f9ea9f9b
- https://gatk.broadinstitute.org/hc/en-us/articles/360037594571-FastaAlternateReferenceMaker
- https://systemsbio.ucsd.edu/perEditor/index.html
- https://github.com/churchill-lab/g2gtools
- https://g2gtools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage.html
- https://github.com/abyzovlab/vcf2diploid
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18852334/construct-dna-sequence-based-on-variation-and-human-reference
