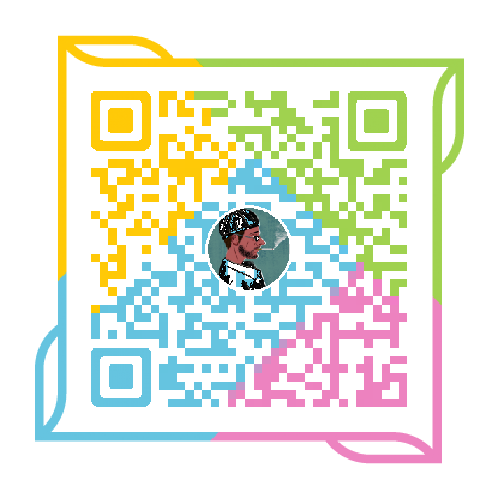
【5.3.3】间接药物设计
Indirect Drug Design:
- Indirect drug design - drug design based on structures and activities of inhibitors, not on the structures of the receptors!
- The basic molecular structures of the inhibitors must be known.
- The active conformation of the compounds must be determined
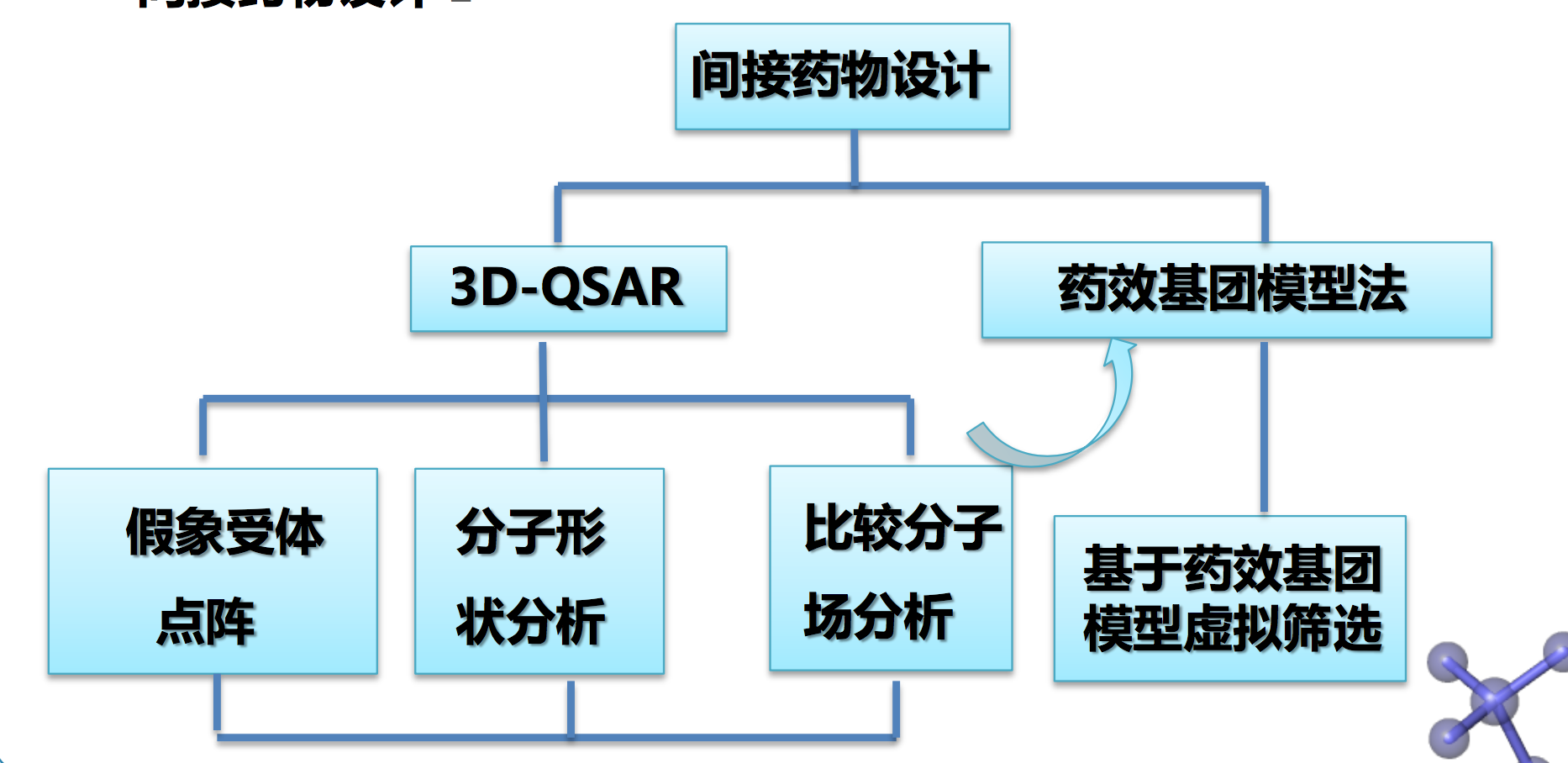
一、基于配体药效团模型的药物设计
药效基团模型法 Pharmacophore modeling
- 对一系列活性化合物进行3D-QSAR研究,并结合构象分析,得出该类 药物的药效基团模型。
- 可在受体三维结构未知的情况下,构造出虚拟的药效基团模型,再由此 出发,进行药物设计。
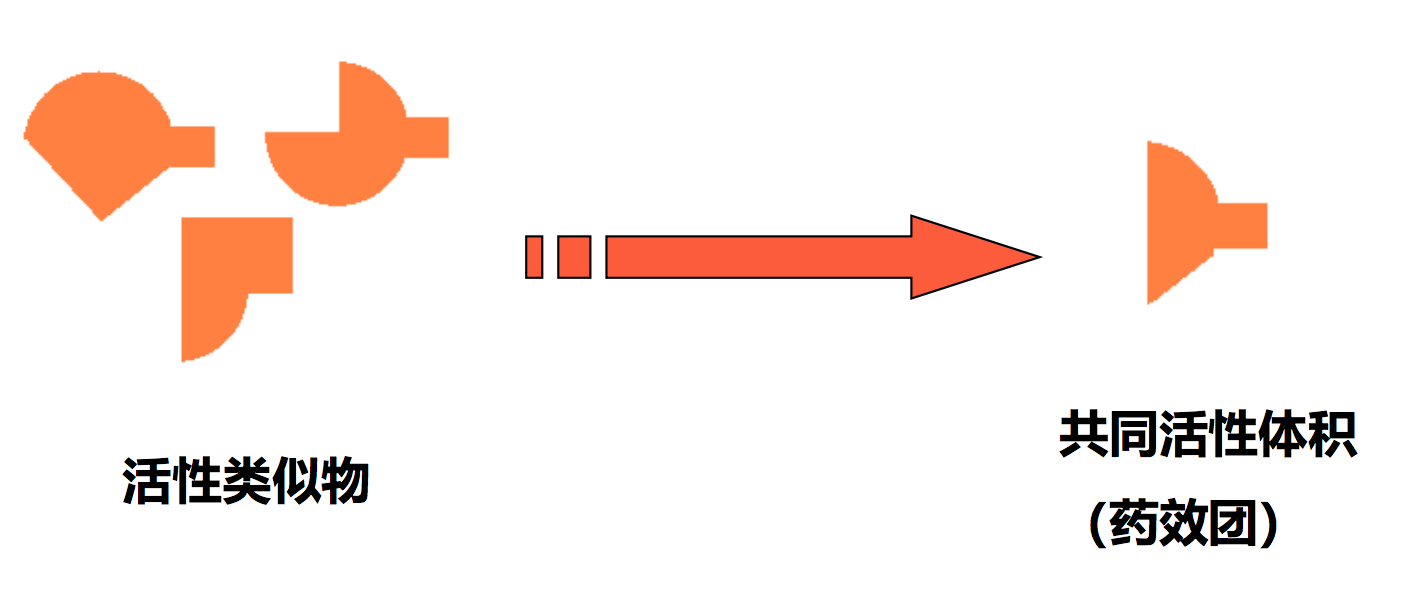
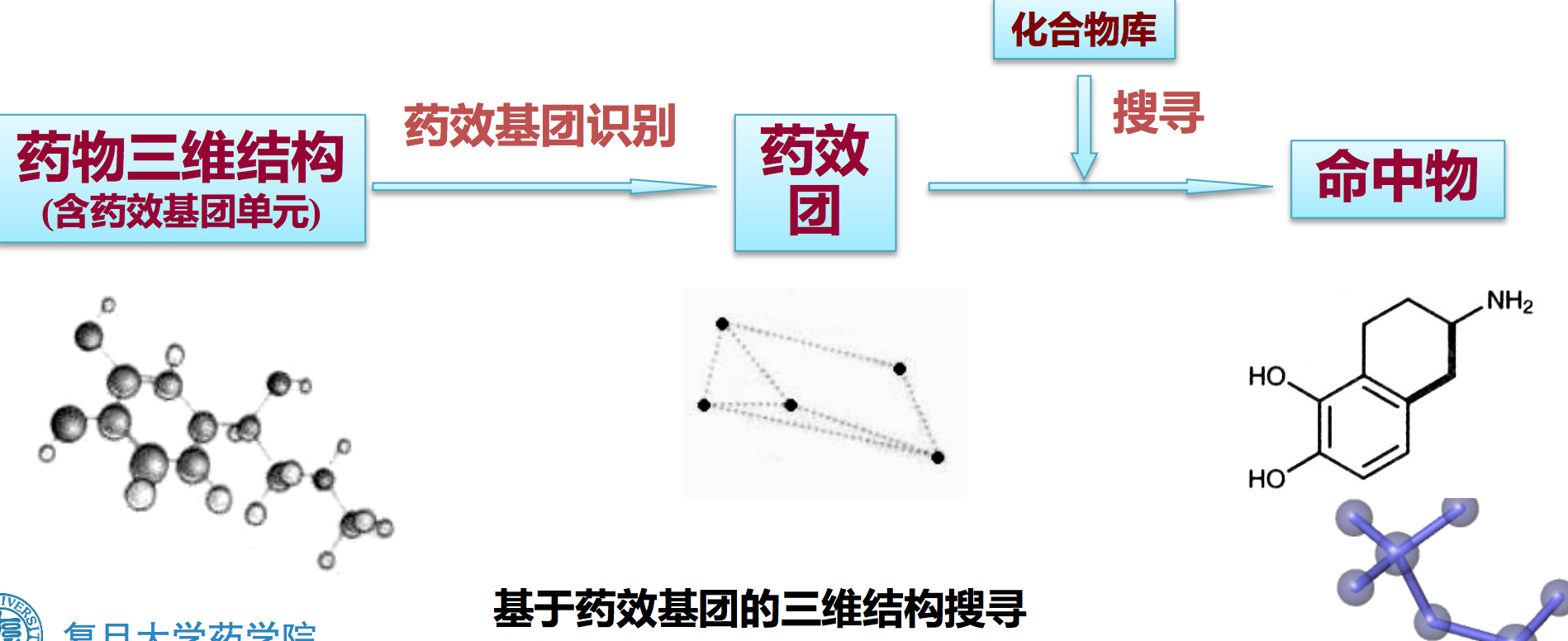
基于配体的药效基团(ligand-based pharmacophore)
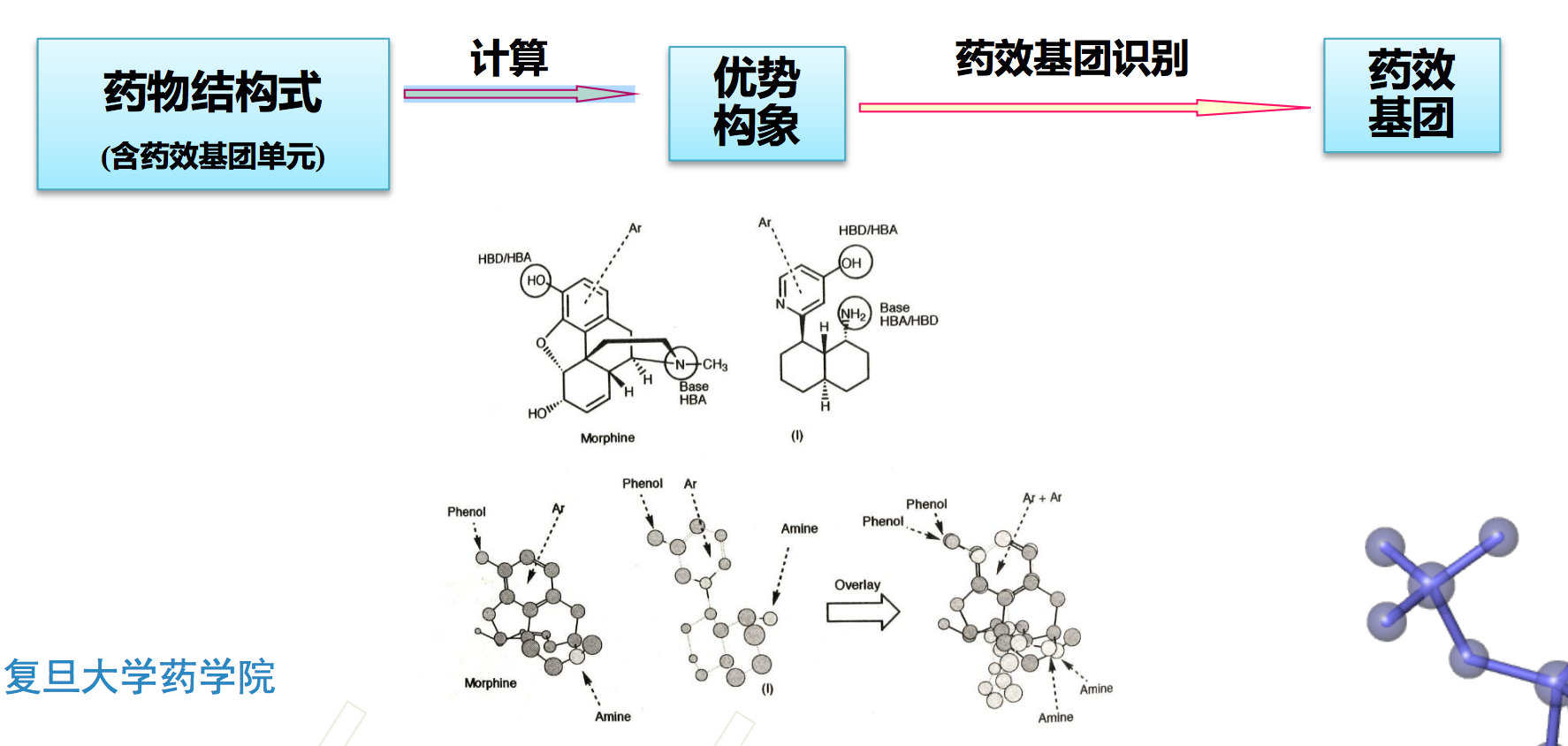
- 药效团是药效基团( pharmacophoric elements )单元的集合
- 药效基团单元 ——组成药效基团所共有的一组原子(团)
- 药效基团单元中的原子或官能团可通过氢键、静电作用、范德华作用和疏水键 等与受体中活性位点发生结合
- 药效基团中的药效基团单元往往用点来定义,若干个点构成平面或空间的结构
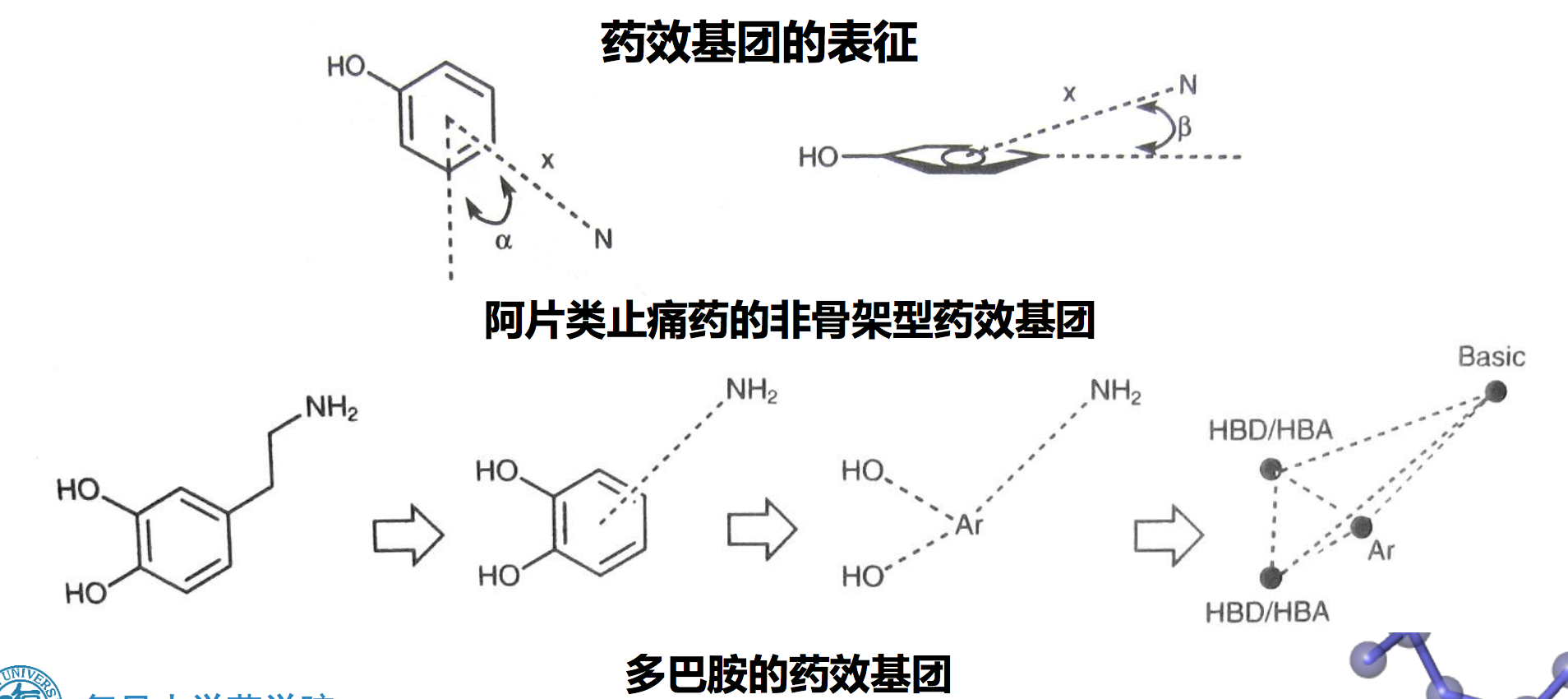
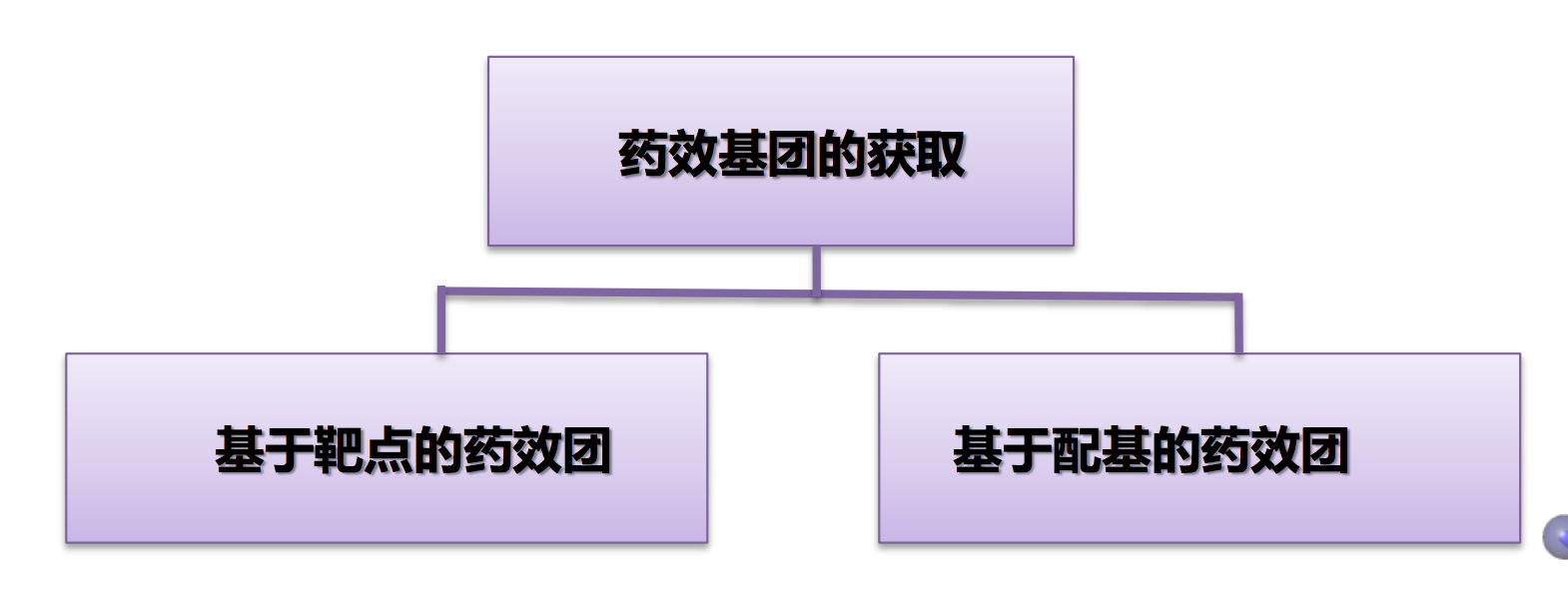
药效基团的获取: Pharmacophore perception

药效基团识别的方法
1. 分子叠合
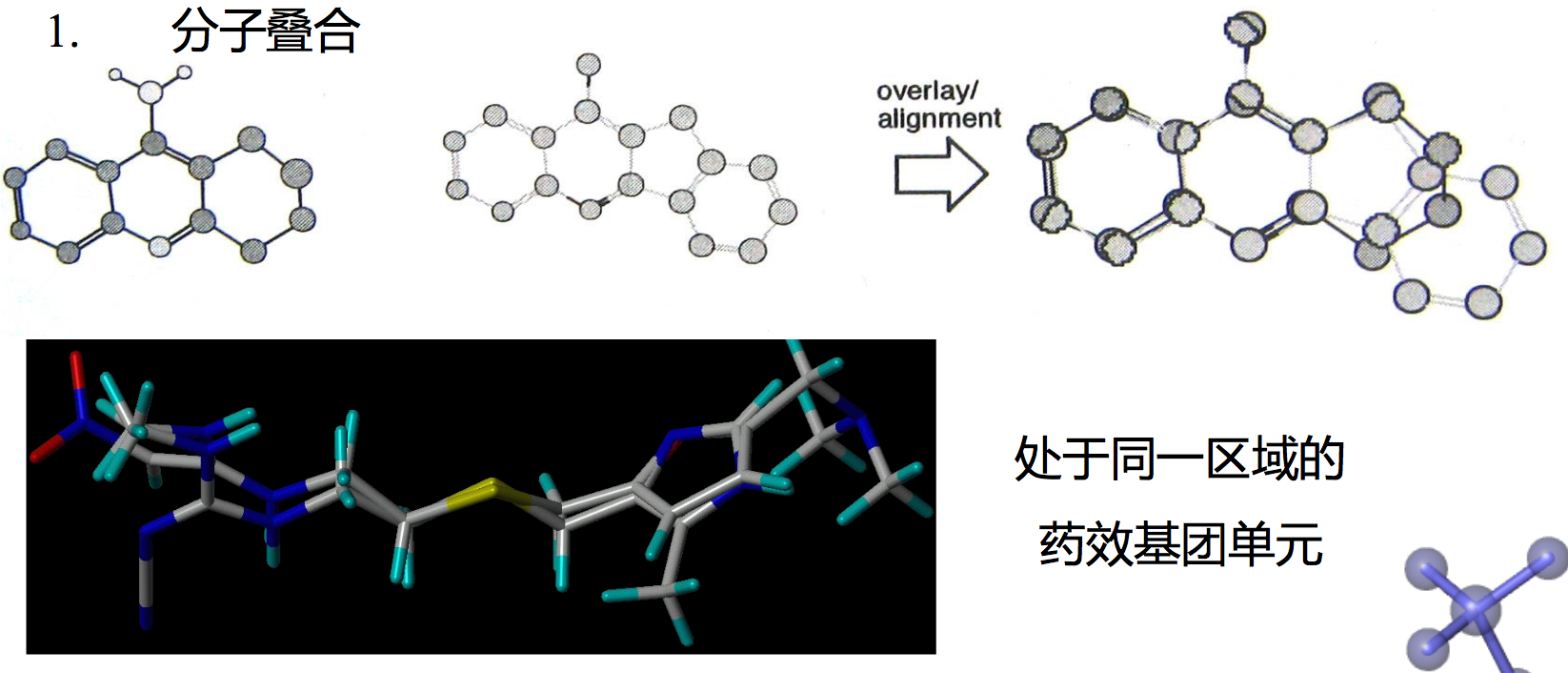
简化方法:最强活性化合物的优势构象
简化方法:刚性药物模板
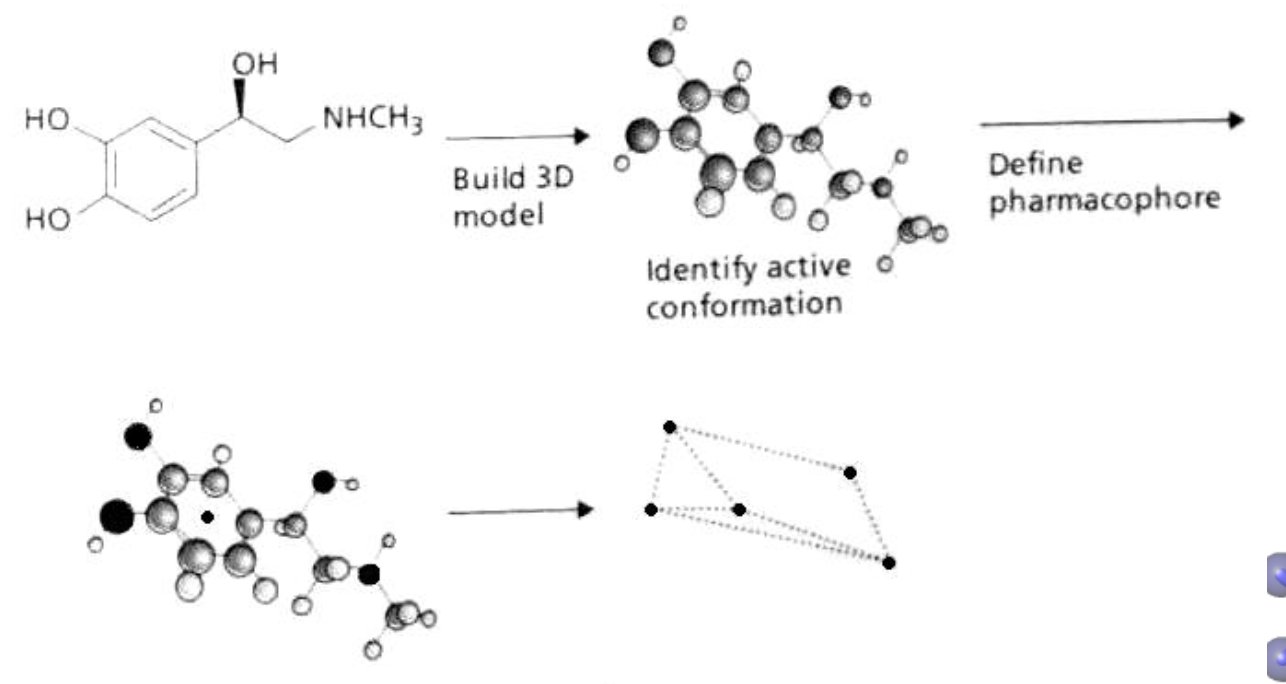
2. 活性类似物法(Active Analogue Approach, AAA)
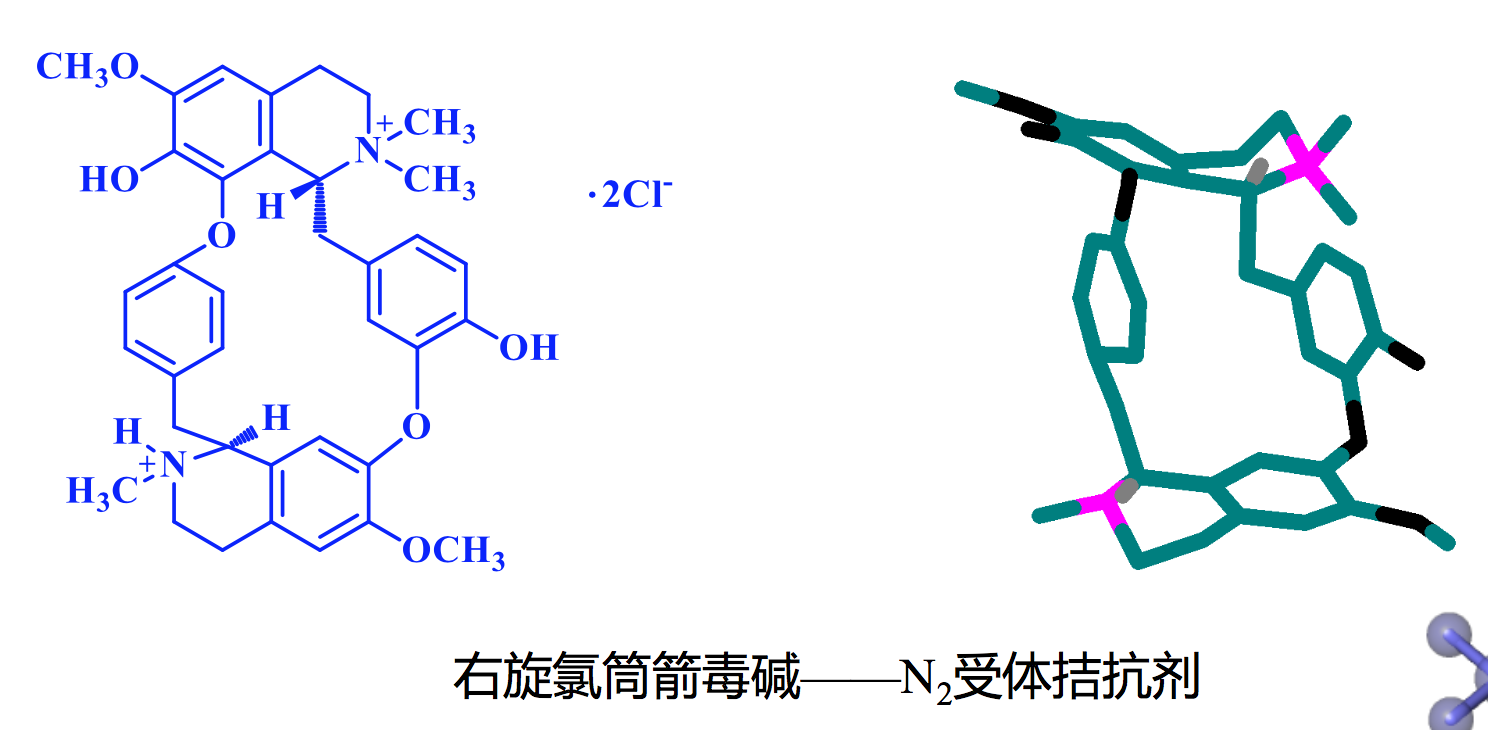
二、基于配体相似性的虚拟筛选(ligand similarity-based virtual screening)
优点:
- 有可能迅速获得化合物的样品进行生物活性测定
缺点:
- 受限于已有的知识
- 所筛选的化合物库中未必有适合给定靶标的配体分子
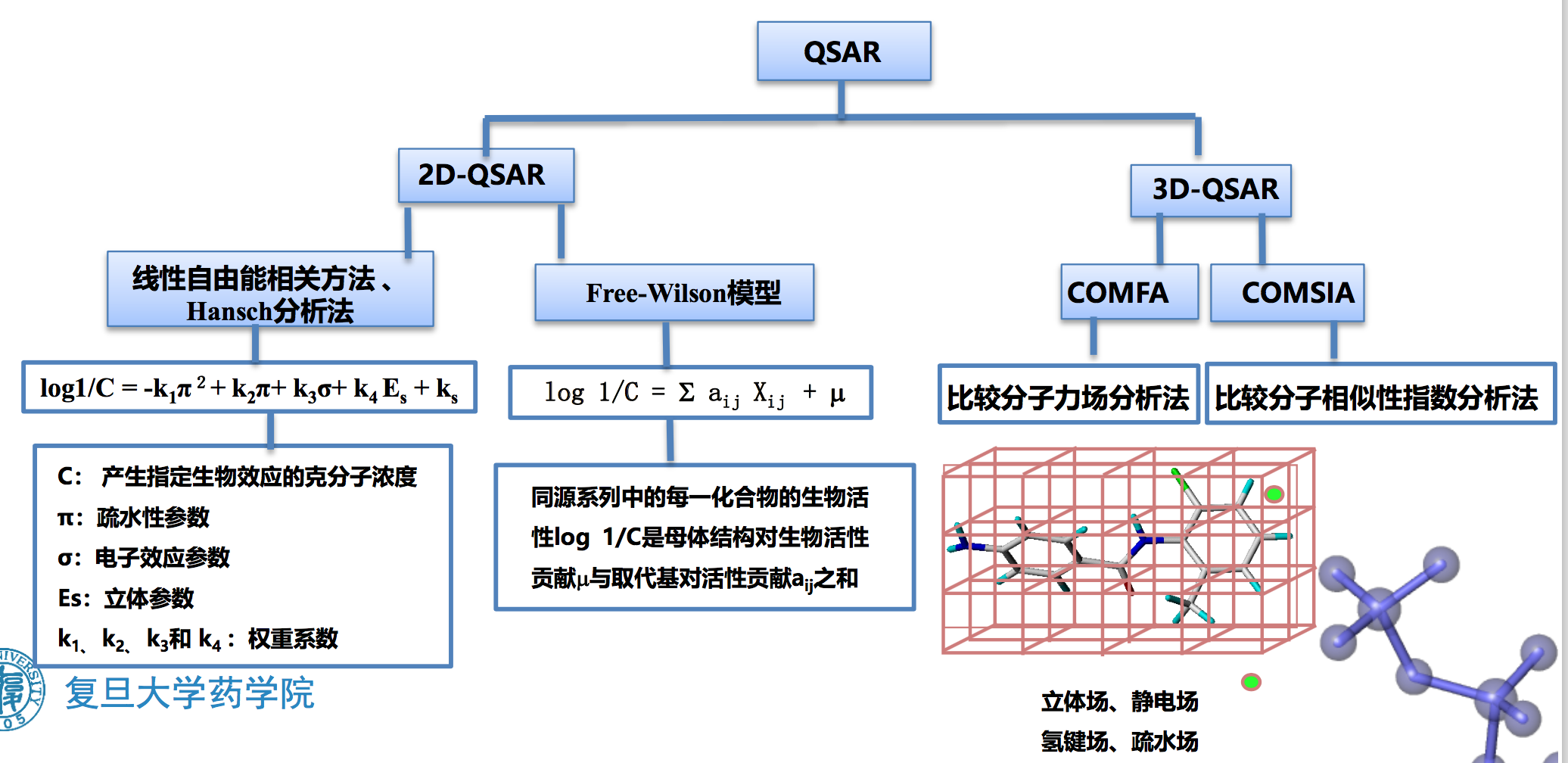
三、基于定量构效关系的药物设计
定量构效关系QSAR —— 揭示一组化合物的生物活性与其分子结构特征之间的相互关系,以数学模型表达和概括出量变规律,以此设计新的化合物
活性 = f (分子或片断性质)
QSAR:
- Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (2D and more recently 3D).
- Attempts are made to identify (non)linear relationships that exist between physical and/or chemical properties (logP, hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity, frontier molecular orbitals (HOMO, LUMO), solubility/free energy of hydration, pKa(s), etc.) and activity (inhibition).
药物设计中的数据统计方法
数据统计——广泛使用计算机的计算和人工智能
- 人工智能 —— 计算机科学中研究使计算机能够模仿智能的某些方面,如识别 、推理、演绎、从经验中学习的能力以及从不完全的信息中进行推理的能力。
数据统计中广泛使用的计算和人工智能
| 回归 / 相关 | MLR(多元线性回归),FW(Free-Wilson模型),FB(Fujita-Ban模型),ALS (适应最小二乘法),PLS(偏最小二乘法)。 |
|---|---|
| 模式识别 / 分类 | PCA(主成分分析),FA(因子分析),SIMCA,DA(判别分析),LLM(线性 学习机法),KNN(K最近邻法),CA(聚类分析),ANN(人工神经网络)。 |
3D-QSAR方法
Three-Dimensional Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships 拟合出药物的理化和三维结构参数与药效的定量关系,以此关系设计新的化合物
Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA)
- CoMFA is a widely-used tool for study of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) at the 3-D level
- 3-D QSAR approaches use statistical methods to correlate the variation in biological or chemical activity with information on 3-D structure for a series of compounds
Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA)
- The underlying idea of the CoMFA is that differences in a target property (e.g. biological activity) are often closely related to equivalent changes in the shapes and strengths of the non-covalent interaction fields surrounding the molecules
- The CoMFA methodology ultimately allows one to design and predict activities of molecules.
3D-QSAR的基本流程

作用能的计算方法
- 测定探针与化合物的相互作用能, 以确定化合物分子周围各种作用力 场(空间场和静电场)的空间分布
- 探针:Csp3, C+

3D-QASR - CoMFA 比较分子力场分析法(Comparative Molecular Field Analysis, CoMFA)

CoMFA 结果的表达形式

CoMSIA (Comparative Molecular Similarity Indices Analysis 比较分子相似性指数分析法
- CoMFA的扩展方法
- 分子场的计算采用5种不同的相似性场计算:
- 立体场
- 静电场
- 氢键场(包括氢键供体和氢键受体)
- 疏水场
- 由于力场考虑更全面,三维构效模型更优
3D-QSAR的优缺点
优点:
- 不必知道靶点的结构
- 不必输入实验测定或理论计算的理化参 数值
- 给出可视图易于解释QSAR结果
- 不限于研究相似分子结构,只须有相同的药效团以相似的方式与靶点作用
- 可预测新分子的活性,而不必先合成
缺点:
- 预测仅限于由训练集包络的空间之内
- 不能可靠地预测出原模型范围之外的
- 取代基结构 ×分析的准确性取决于采用的空间结构
参考资料
- 复旦大学 李伟 老师的 《药物设计学》 课件
这里是一个广告位,,感兴趣的都可以发邮件聊聊:tiehan@sina.cn
![]() 个人公众号,比较懒,很少更新,可以在上面提问题,如果回复不及时,可发邮件给我: tiehan@sina.cn
个人公众号,比较懒,很少更新,可以在上面提问题,如果回复不及时,可发邮件给我: tiehan@sina.cn

